A tachometer is a crucial instrument used in vehicles to measure the speed of the engine. For you to understand why this device is so important, this article will dive deeply into every aspect of a tachometer. It will help you grasp the significance, working principles, types, and benefits of having a tachometer in your car.
In this article, we will cover the following major points about a tachometer:
- What is a Tachometer?
- How Does a Tachometer Work?
- Importance of Having a Tachometer in Your Car
- Different Types of Tachometers
- The Mechanism Behind a Tachometer
- The Role of a Tachometer in Engine Performance
- Installation and Maintenance of a Tachometer
- How to Read a Tachometer?
- FAQs
What is a Tachometer?
A tachometer is an instrument that measures the rotation speed of the engine’s crankshaft. Typically, it is displayed in RPM (Revolutions Per Minute). The device helps monitor engine performance and ensures it is running within safe limits.
The word ‘tachometer’ comes from the Greek words ‘tachos’ meaning speed, and ‘metron’ meaning measure. These instruments have been around for over a century, initially used in steam engines before being incorporated into automobiles.
How Does a Tachometer Work?
A tachometer works by measuring the frequency of the pulses generated by the ignition system of the engine. In simpler terms, it counts each time the crankshaft completes a rotation.
Modern digital tachometers use sensors and electronic circuits to provide accurate readings. They can be found in dashboards of almost all modern cars, providing real-time engine speed data to the driver.
Importance of Having a Tachometer in Your Car
Having a tachometer in your car is indispensable for several reasons. Firstly, it allows you to monitor the engine speed, ensuring that you are not over-revving the engine, which can cause significant damage over time. It also helps in achieving better fuel efficiency by maintaining optimal engine speeds during different driving conditions.
Additionally, a tachometer is crucial for manual transmission vehicles. It aids in smoother gear shifts, reducing wear and tear on the engine.
Different Types of Tachometers
Analog Tachometers
Analog tachometers have a needle pointing to a scale that indicates the RPM. These are the traditional types and are commonly found in older vehicles.
Digital Tachometers
Digital tachometers provide a numeric display of the RPM. They are more accurate and easier to read compared to analog counterparts. These are increasingly being used in modern vehicles.
Contact and Non-Contact Tachometers
Contact tachometers require physical touch with the engine to measure its speed, while non-contact tachometers use sensors to measure without direct contact. Non-contact types are more convenient and safer to use.
The Mechanism Behind a Tachometer
The mechanism of a tachometer involves several components that work together to accurately measure and display engine speed. These include sensors, electronic circuits, and display units.
The sensors detect the rotational speed of the engine. This data is then processed by electronic circuits, which convert it into readable output displayed on the dashboard.
The Role of a Tachometer in Engine Performance
A tachometer plays a vital role in engine performance. By providing real-time data on engine speed, it helps drivers maintain optimal driving conditions. This not only enhances performance but also prolongs the engine’s lifespan.
Moreover, it aids in diagnosing potential engine problems early, allowing for timely maintenance and repairs.
Installation and Maintenance of a Tachometer
While most modern cars come with pre-installed tachometers, installing one in an older vehicle requires technical expertise. It involves connecting the device to the engine’s ignition system and ensuring proper calibration.
Maintenance of a tachometer includes regular checks to ensure accuracy. Faulty sensors or connections can result in inaccurate readings, which can be detrimental to engine health.
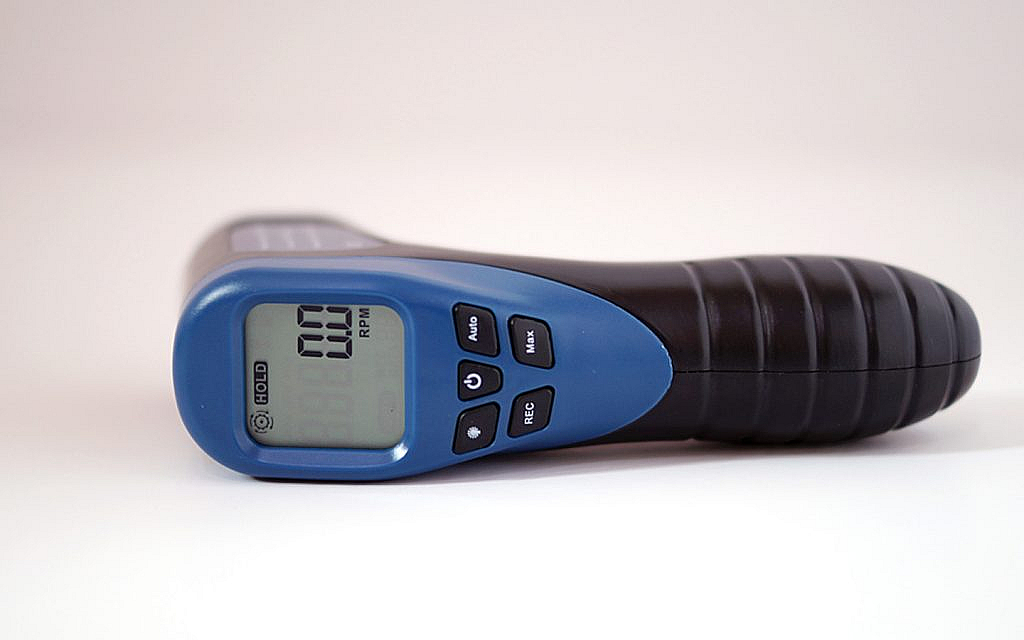
How to Read a Tachometer?
Reading a tachometer is straightforward. The RPM is displayed on the meter’s scale or digital display. The red line on the tachometer indicates the maximum safe engine speed. Going beyond this limit can cause engine damage.
By keeping an eye on the tachometer, drivers can ensure they are operating within safe engine speed parameters.

FAQs
1. What is the purpose of a tachometer in a car?
A tachometer measures the engine’s rotational speed, helping drivers maintain optimal performance and preventing damage from over-revving.
2. How does a tachometer improve fuel efficiency?
By monitoring engine speed, a tachometer helps drivers maintain optimal RPM levels, leading to better fuel efficiency.
3. Can a tachometer help in diagnosing engine issues?
Yes, unusual RPM readings on a tachometer can indicate potential engine issues, allowing for early diagnosis and repair.
4. Is it easy to install a tachometer in a car?
Installing a tachometer can be complex and typically requires technical expertise, particularly in older vehicles.
5. What are the types of tachometers?
Tachometers come in analog, digital, contact, and non-contact types, each with its specific advantages and applications.
For more detailed information on tachometers and their working mechanism, you can refer to this How Does a Tachometer Work link.
Additionally, you can explore our various event detection, paint inspection, and genetic analysis articles to find more technical insights.