Calibrating a tachometer is a crucial process for ensuring accurate measurements in various industrial applications. Whether you are working in automotive, manufacturing, or quality assurance, knowing how to calibrate a tachometer effectively can make a tremendous difference. In this article, we will take a detailed look into the steps and considerations involved in the calibration process, providing you with a comprehensive, technology-approved guide.
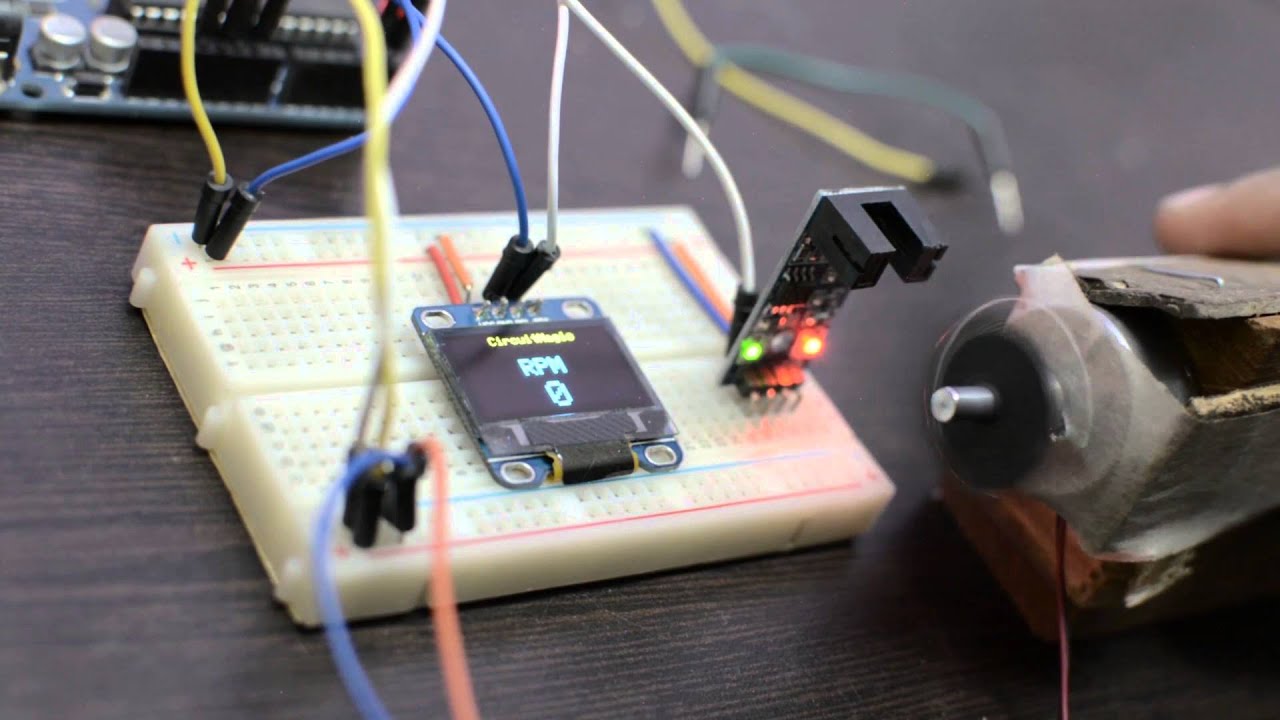
What is a Tachometer?
A tachometer is an instrument that measures the rotational speed of an object. It is commonly used in cars, aircraft, and industrial machinery to monitor performance. Understanding its purpose is the first step in learning how to calibrate a tachometer.
Types of Tachometers
Tachometers come in various types, including digital, analog, and contact or non-contact types. Each type has its own calibration procedures and requirements.
Why Calibration is Important
Calibration ensures that the tachometer provides accurate readings, which are essential for maintaining equipment performance and safety. Regular calibration helps in avoiding costly repairs and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Initial Setup
Before you start the calibration process, gather all necessary tools and documentation. This includes the tachometer’s user manual, a reliable calibration tool, and any software required for digital tachometers.
Safety Precautions
Always follow safety guidelines when handling electrical instruments. Wear protective gear and ensure the workspace is free from hazards.
Calibration Procedures
Depending on the type of tachometer, the calibration process may vary. Generally, it involves the following steps:
Analog Tachometers
- Connect the tachometer to a known speed source.
- Adjust the tachometer’s needle to match the known speed.
- Verify the readings at different speeds.
Digital Tachometers
- Connect the tachometer to a calibrated speed source.
- Use the software to adjust and verify the readings.
- Save the calibration settings.
Verification and Testing
After calibration, it is essential to test the tachometer to ensure accuracy. Run the machine at different speeds and compare the readings with the known source.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Sometimes, calibration may not go as planned. Common issues include incorrect readings, software glitches, and electrical problems. Refer to the user manual or consult a professional for troubleshooting tips.
Maintaining Calibration
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your tachometer calibrated. Schedule periodic checks and recalibrations to ensure consistent performance.
Professional Calibration Services
For those who may not have the tools or expertise, professional calibration services are available. These services ensure that your tachometer is calibrated to industry standards.
Advanced Techniques
For more advanced applications, such as high-speed genetic analysis and sequencing monitoring, specialized calibration techniques may be required. These techniques ensure precision and accuracy in demanding environments.
Explore more about advanced stroboscopic event detection in semiconductor wafer polishing on our advanced stroboscopic event detection page.

FAQs
How often should a tachometer be calibrated?
It depends on the usage and manufacturer’s recommendations. Generally, yearly calibration is recommended.
Can I calibrate a tachometer myself?
Yes, with the right tools and knowledge, you can calibrate a tachometer yourself. However, professional services are also available.
What are common signs that my tachometer needs calibration?
Inaccurate readings and inconsistent performance are common signs that your tachometer requires calibration.
For more detailed information, you can refer to this [external link](https://www.britannica.com/technology/tachometer).
