For many people, understanding how to set a tachometer can seem daunting. However, it’s a task that can be made easy with the right guidance. In this article, we walk you through the steps to achieve an accurate setup of your tachometer, ensuring it works perfectly with approved technology tips to maximize your equipment’s performance.
A tachometer is a crucial device that measures the rotational speed of a shaft or disk, as in a motor or other machine. It typically displays the revolutions per minute (RPM). Understanding how to properly set a tachometer ensures that the machine runs smoothly and prevents potential mechanical failures.

What is a Tachometer?
A tachometer is an instrument used to measure the rotation speed of any rotating object. Its primary purpose is to provide valuable information about the performance and functioning of machinery, particularly in automotive and industrial applications. To dive deeper into this topic, visit this detailed page on tachometers.
Types of Tachometers
- Analog Tachometers
- Digital Tachometers
- Contact Tachometers
- Non-Contact Tachometers
Why is Setting Up Your Tachometer Important?
Correctly setting up your tachometer is vital for various reasons:
- Accurate measurement: Ensures the rotational speed is measured correctly.
- Performance monitoring: Helps in keeping track of machine performance and efficiency.
- Prevention of failures: Early detection of irregularities to prevent mechanical failures.
Prerequisites for Setting Up a Tachometer
Before we start with the actual setup process, ensure you have the following:
- The tachometer device
- User manual
- Basic tools for installation
- Calibration equipment
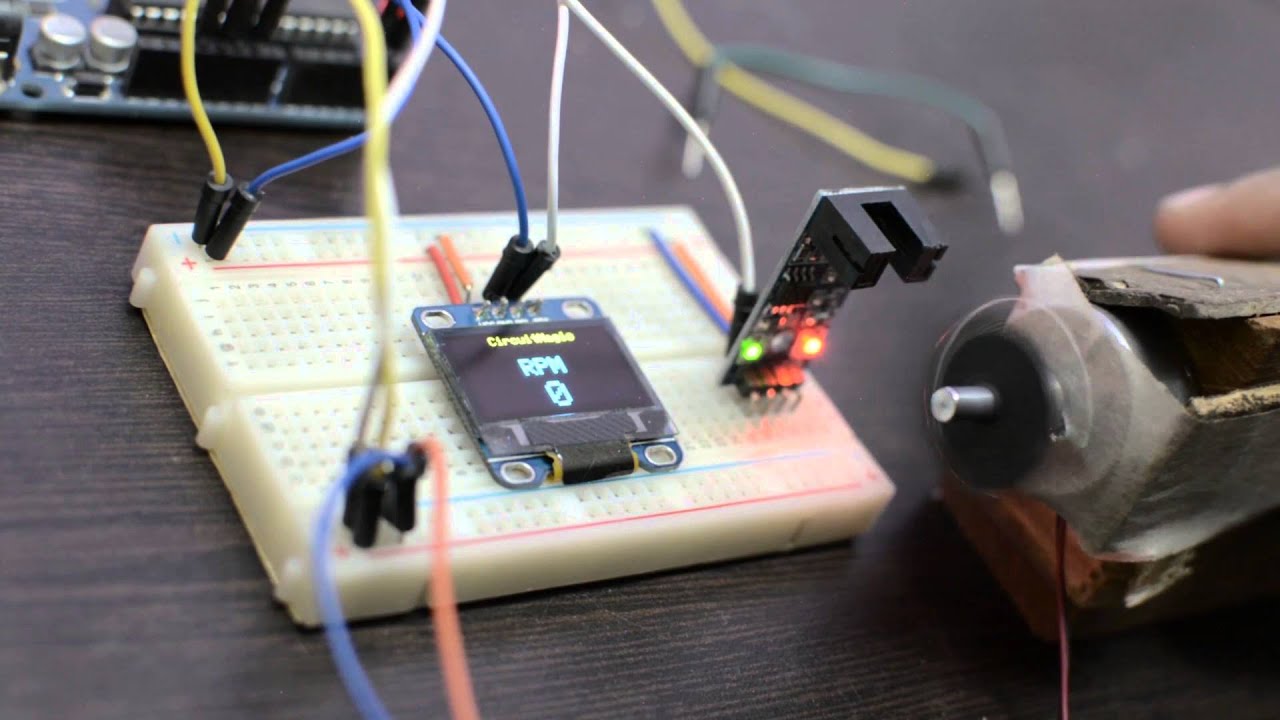
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Set Tachometer
Step 1: Reading the User Manual
The first step is to thoroughly read the user manual that comes with the tachometer. This manual provides specific instructions related to the device you are using, ensuring you are familiar with all its features and functionalities.
Step 2: Preparing for Installation
Before installing the tachometer, ensure that the setup location is clean and all connections are secure. This step also includes gathering the necessary tools needed to install the device.
- Screwdrivers
- Wrenches
- Electrical tape, etc.
Step 3: Installing the Tachometer
Follow the user manual’s instructions to install the tachometer. Typically, this will involve mounting the device securely to the machine, connecting it to the power source, and linking it with other necessary components.
- Mounting location: Choose a place where the device is easily visible and accessible.
- Wiring connections: Connect the power wires carefully, ensuring there are no loose ends.
Step 4: Calibrating the Tachometer
Once installed, calibrate the tachometer to ensure accurate readings. Calibration involves adjusting the device to align with a known standard or reference. This step might require specific calibration tools or software.
Visit Paint Inspection to see how accurate calibration is crucial in different applications.
Step 5: Testing the Tachometer
After calibration, test the tachometer by running the machine at different speeds and checking if the readings are accurate. This step helps verify the setup and ensure the device is functioning correctly.
Common Issues While Setting Tachometers
Incorrect Readings
One of the common issues you may encounter is incorrect RPM readings. This could be due to improper installation or calibration.
Fluctuating Measurements
If the tachometer shows fluctuating measurements, it could result from loose connections or external interferences.
Maintaining Your Tachometer
Proper maintenance of the tachometer is key to ensuring its longevity and accurate performance.
- Regular cleaning
- Periodic calibration checks
- Inspection for wear and tear
Advanced Tachometer Technologies
Modern tachometers come with advanced technologies to improve accuracy and usability.
Digital Displays
Many tachometers now come with digital displays for easier and more precise readings.
Wireless Connectivity
Some devices offer wireless connectivity, allowing remote monitoring and adjustments.
For more advanced technology applications, visit Event Detection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What types of tachometers are used in different industries?
Different industries use various types of tachometers based on their specific requirements. For example, automotive industries use digital tachometers, while manufacturing sectors prefer analog ones for certain applications.
How often should tachometers be calibrated?
It is advisable to calibrate tachometers periodically, depending on the device’s usage and manufacturer’s recommendations. Regular calibration ensures continued accuracy.
Can I set a tachometer by myself?
Yes, most tachometers come with user-friendly manuals that guide you through the setup process. However, for complex setups, consulting a professional is recommended.
For detailed consultancy, you can check Technology Insights.
