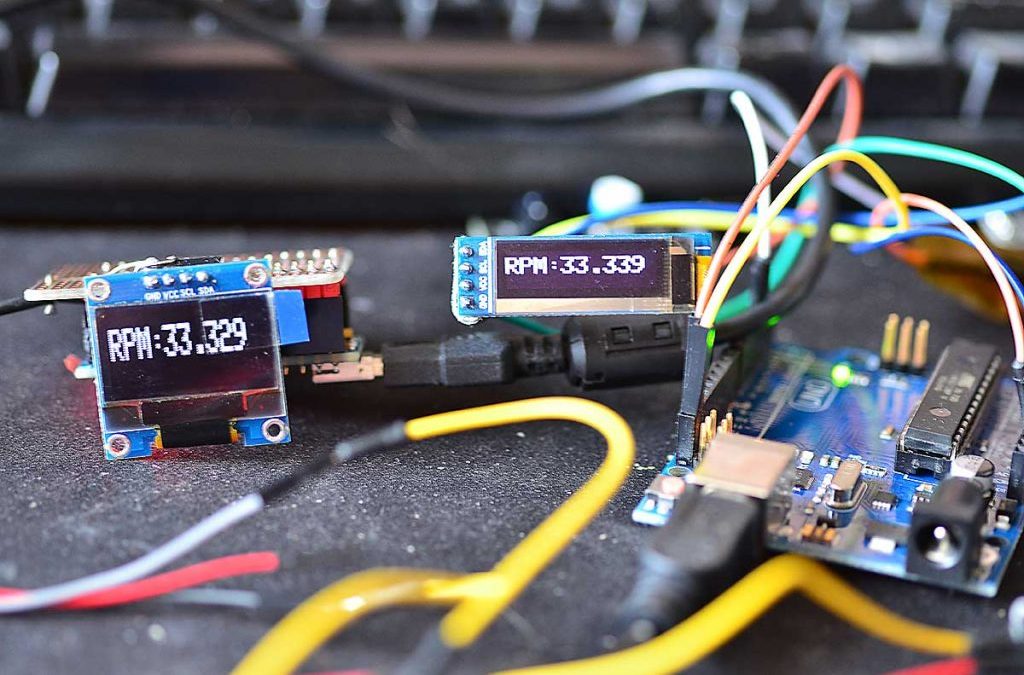
Testing a vintage tachometer can be an exciting and meticulous process. Vintage tachometers are essential instruments, particularly in classic cars, motorcycles, and aviation. Ensuring their accuracy and reliability is crucial. In this article, we’ll cover how to test a vintage tachometer using technology and a few approved techniques.
Unlike modern digital tachometers, vintage tachometers operate on analog mechanisms. Thus, understanding how they function is crucial for accurate testing.
Understanding the Basics of Vintage Tachometers
Before diving into the testing process, it is essential to understand how a vintage tachometer works.
What is a Vintage Tachometer?
A vintage tachometer measures the rotational speed of an engine shaft. Typically, it displays the RPM (revolutions per minute). This instrument is especially vital in classic vehicles where engine performance monitoring is crucial.
Key Components
- Mechanical Drive
- Needle and Dial
- Magnetic Coupling
- Spring Mechanism
Knowing these components helps in identifying potential issues during testing.
Why Test a Vintage Tachometer?
Testing ensures accuracy. Inaccurate readings can lead to various problems, such as engine damage or performance inefficiencies. Regularly testing the instrument assures its reliability.
Common Issues in Vintage Tachometers
- Inaccurate Readings
- Needle Sticking
- Magnetic Interference
- Wear and Tear
Preparing for the Test
Preparation is key. Below is a checklist to start the testing process:
Gather Necessary Tools
- Multimeter
- Calibrated Tachometer for Reference
- Screwdrivers
- Lubricating Oil
- Cleaning Materials
Initial Inspection
Start with a visual inspection:
- Check for Physical Damage
- Ensure the Dial and Needle Move Freely
- Inspect for Rust or Debris
How to Test a Vintage Tachometer: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Calibration Check
Calibration ensures the tachometer’s accuracy. Compare the readings of the vintage tachometer with a modern, calibrated one.
Step 2: Electrical Connectivity
Use a multimeter to check the connectivity. Ensure that there are no broken circuits.
Step 3: Magnetic Coupling
Inspect the magnetic coupling mechanism for wear and tear. Ensure it’s not causing any interference or sticking.
Step 4: Spring Mechanism
Check the spring mechanism for tension and elasticity. A worn-out spring can lead to inaccurate readings.
Step 5: Lubrication
Lubricate moving parts to ensure smooth operation. Use appropriate lubricating oil recommended for metallic parts.
Advanced Testing Techniques
Bench Testing
Remove the tachometer from the vehicle and set it up on a test bench. This allows for controlled testing without external influences.
Oscilloscope Analysis
Use an oscilloscope to analyze the tachometer’s signal output. This advanced method provides more detailed insights into performance.
Reassembling and Final Checks
After testing, reassemble the tachometer and conduct a final check to ensure everything is in working order.
Trusted Resources
For more information, check out this detailed guide.
Internal Links for Additional Insights
FAQ
What is a vintage tachometer?
A vintage tachometer is a device used to measure the rotational speed of an engine shaft, typically found in classic vehicles.
How often should I test my vintage tachometer?
Regular testing, ideally once every six months, ensures its accuracy and reliability.
Can I test a vintage tachometer at home?
Yes, with the right tools and guidance, you can perform some basic tests at home.
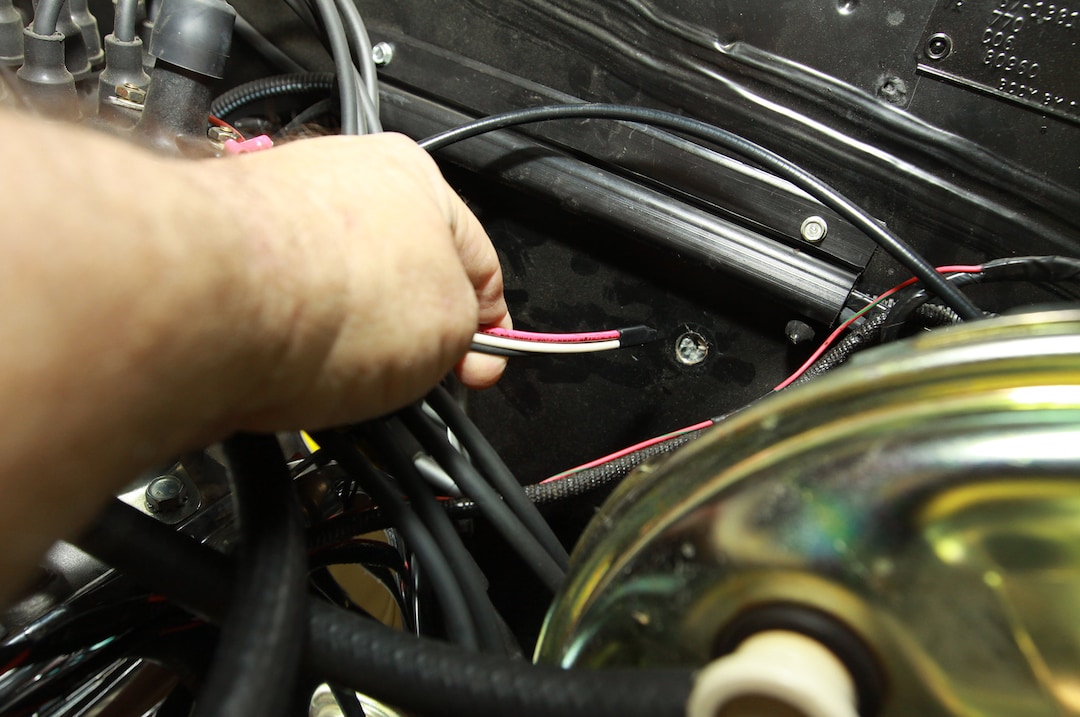
Conclusion
Testing a vintage tachometer is vital for ensuring the performance and longevity of engines in classic vehicles. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can ensure your vintage tachometer is in optimal working condition.