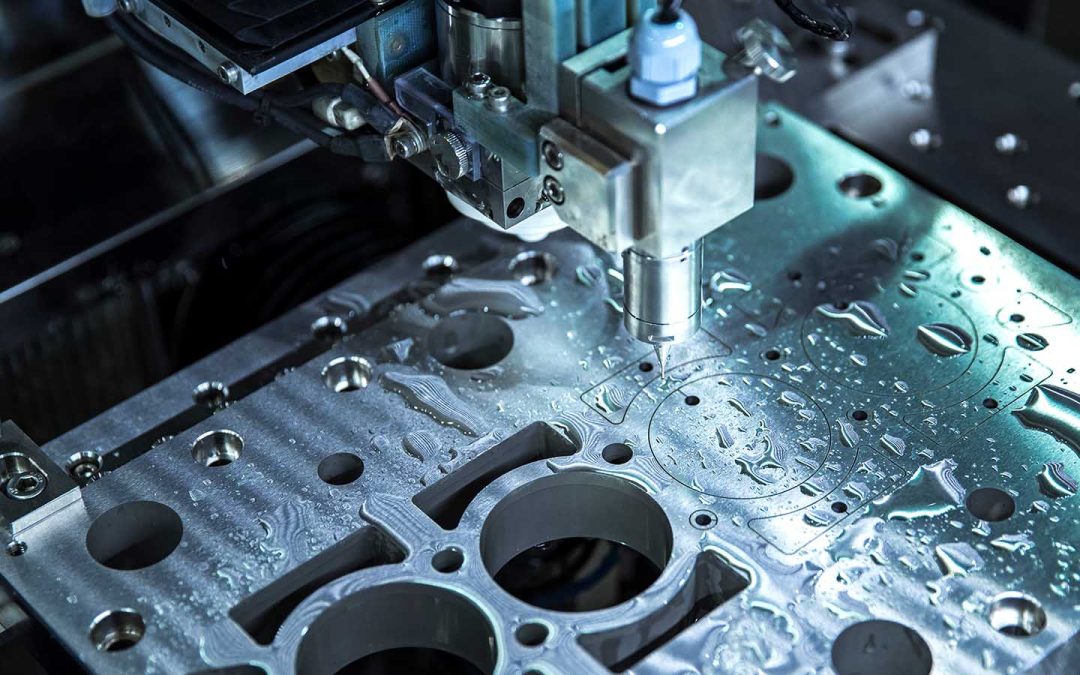
Ensuring that your milling machine is properly calibrated is essential for achieving high precision and productivity. In this article, we’re delighted to present a comprehensive guide on how to calibrate a milling machine. This will help industry QA professionals achieve tremendous results in their machining processes.

Why Calibration is Important
Calibration is a critical component in the maintenance of a milling machine. It ensures accuracy, reduces the risk of errors, and prolongs the life of the machine. A well-calibrated machine is a cornerstone for delivering precise work, leading to higher customer satisfaction and lower production costs.
Understanding Milling Machine Calibration
Calibration involves fine-tuning the settings of your milling machine to meet specific tolerances. This process involves adjusting various mechanical and electronic components to ensure that the machine operates at optimal levels.
Initial Checks Before Calibration
Before beginning the calibration process, it is crucial to perform initial checks. These include:
- Inspecting the machine for any visible wear and tear.
- Ensuring that the machine is clean and free of debris.
- Verifying that all tools and measuring instruments are in good condition.
Cleaning the Milling Machine
A clean milling machine is essential for accurate calibration. Accumulated dirt and debris can affect the machine’s performance and lead to incorrect measurements. Use appropriate cleaning agents and tools to clean the machine thoroughly.
Gathering Necessary Tools and Equipment
To properly calibrate a milling machine, you will need the following tools:
- Calipers
- Dial indicators
- Feeler gauges
- Precision straightedge
- Wrenches and screwdrivers
Checking the Spindle
The spindle is a critical part of the milling machine that requires precise calibration. Use a dial indicator to measure the runout of the spindle and make necessary adjustments.
Adjusting the Machine Bed
The machine bed must be flat and level to ensure accurate milling. Use a precision straightedge and feeler gauges to check the flatness of the bed. If adjustments are needed, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for making these corrections.
Aligning the Axis
Alignment of the machine’s axes (X, Y, and Z) is crucial for precise milling. Use a dial indicator to check the alignment and make necessary adjustments to ensure that each axis is perpendicular to the others.
Calibration of the Digital Readout (DRO)
The digital readout (DRO) provides real-time feedback on the position of the machine’s tool. Calibrating the DRO involves:
- Setting the DRO to zero at a known reference point.
- Moving the machine to a secondary reference point.
- Verifying that the DRO readings correspond to the actual movement of the machine.
Checking Squareness
Ensuring that the milling machine is square is vital for achieving accurate cuts. Use a machinist’s square to check the squareness of the machine and make any necessary adjustments.
Re-Calibrating After Tool Changes
Whenever a tool is changed, it is essential to re-calibrate the milling machine to account for any differences in tool length or diameter. This will ensure that the machine continues to deliver precise results.
Regular Maintenance and Checks
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping the milling machine in top condition. Perform routine checks and follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule to ensure the longevity and accuracy of the machine.
Common Calibration Issues and Solutions
During the calibration process, you may encounter some common issues. Here are a few problems and their solutions:
- Inaccurate Measurements: Verify the accuracy of your measuring instruments and recalibrate if necessary.
- Machine Vibration: Check for loose components and secure them properly.
- Tool Wear: Replace worn tools to maintain accuracy.
Using Calibration Software
Calibration software can automate many aspects of the calibration process, making it easier and more efficient. Investing in good calibration software can save time and improve accuracy.
Training for Machine Operators
Proper training for machine operators is essential for maintaining accurate calibration. Ensure that all operators are trained in calibration procedures and understand the importance of regular calibration checks.
Documenting Calibration Procedures
Documenting the calibration procedures is vital for consistency and accountability. Keep detailed records of all calibration activities, including the tools used, measurements taken, and any adjustments made.
Conclusion
Calibrating a milling machine is a critical component of machine maintenance that ensures accuracy and prolongs the life of the machine. By following the steps outlined in this guide, industry QA professionals can achieve tremendous results in their machining processes.
FAQs
- Q1: How often should I calibrate my milling machine?
-
A1: It is recommended to calibrate your milling machine at least once every six months or whenever you notice a decline in accuracy.
- Q2: What are the signs that my milling machine needs calibration?
-
A2: Some signs include inaccurate cuts, machine vibrations, and visible wear on tools. Regular checks can help detect these issues early.
- Q3: Can I use calibration software for my milling machine?
-
A3: Yes, calibration software can automate many aspects of the calibration process and improve accuracy and efficiency.
For more information, you can visit CNC Masters.
Check out some High-Speed Genetic Analysis & Sequencing for further insights on CNC machine applications.
More information on High-Speed Wafer Polishing is also available for your reference.
If you’re curious, you might be interested in exploring High-Speed Manufacturing Inspections related to CNC machines.