The milling machine is one of the most essential tools in the manufacturing industry. If you are new to milling machines, you might be asking: What are the parts of milling machine? Knowing the answer to this is important as it can tremendously help in machine maintenance and troubleshooting problems. In this article, we are delighted to dive deep and explain all the major parts of a milling machine.
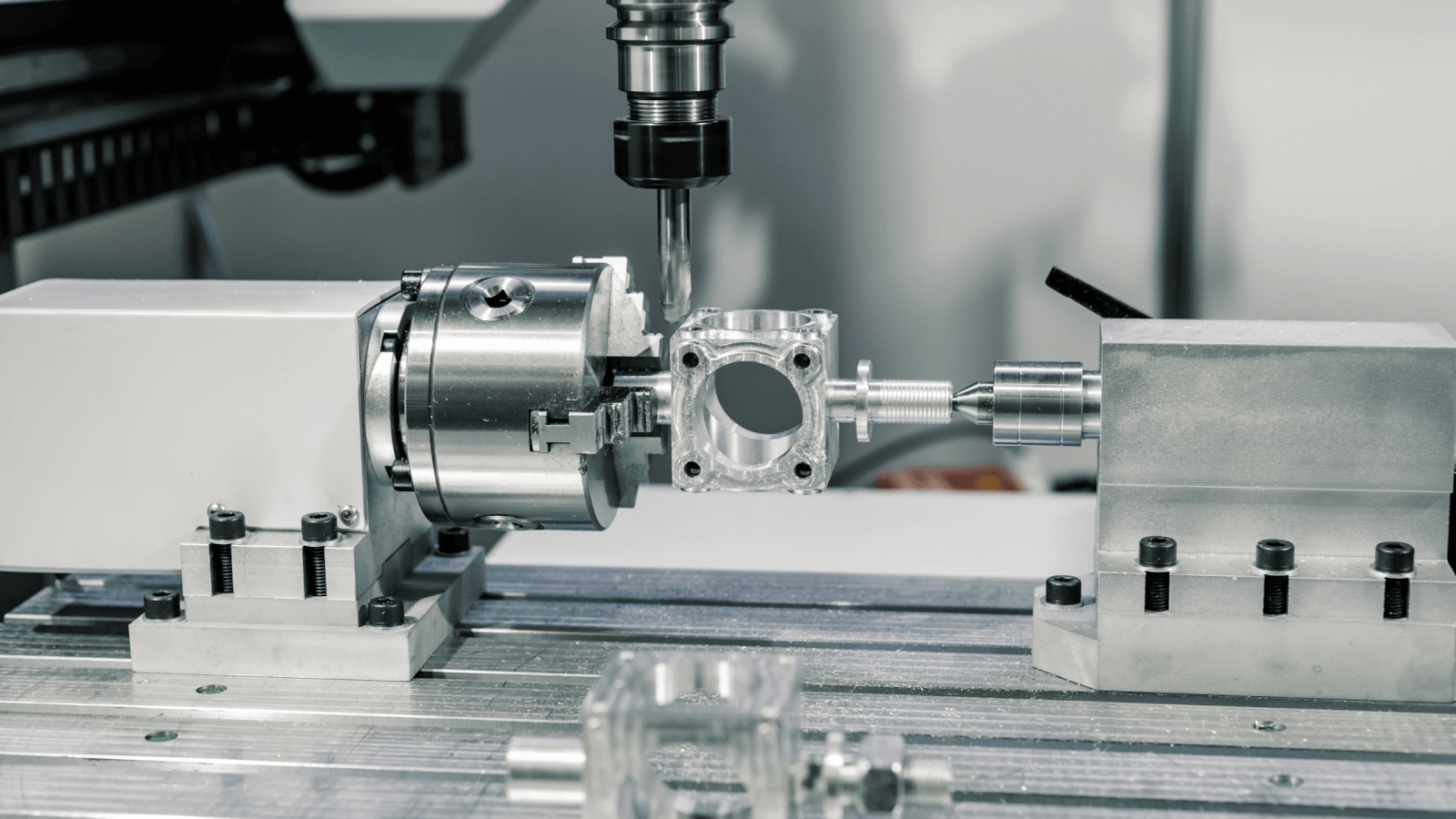
Base and Column
The base and column of a milling machine are the foundation upon which the entire structure is built. The base serves as the machine’s primary support, typically made of cast iron. It not only supports the machine but also absorbs the vibrations produced during milling.
The Column
The column is vertically mounted on the base and is another crucial part. The column housing includes the drive mechanism, gearing, and quill. Columns provide stability and rigidity to ensure precision during milling.
Knee
The knee is mounted on the column and can move up and down on the column ways. The knee is significant for controlling the vertical movement of the machine’s components, adding to the flexibility in machining various shapes and sizes.
The Control Mechanism
The knee height is commonly adjusted by a vertical positioning screw. This control allows you to alter the vertical position of the table and workpiece, offering tremendous flexibility in operations.
Saddle and Swivel Table
The saddle is a part of the milling machine found on top of the knee. It moves perpendicular to the column and provides support to the table and its movement along the Y-axis.
The Swivel Table
The swivel table plays a vital role in adjusting the angle of the workpiece. Why is this feature important? It helps in machining angled surfaces and making complex cuts more manageable. The saddle moves the table along the Y-axis, increasing machining versatility.
Power Feed Mechanism
The power feed mechanism automates the movement of the table along the X, Y, and Z axes. This enables more consistent and less labor-intensive milling, increasing productivity substantially. The power feed often includes speed control features to adapt to different materials and machining requirements.
Main Components
Among the main components of the power feed mechanism are the gearbox, motor, and lead screw. These parts work together to ensure smooth and precise control over the tables movement.
Milling Head
The milling head is one of the most dynamic components of the milling machine. It houses the spindle, motor, and various gears and settings. The milling head can be adjusted to different heights and angles, providing additional machining capabilities. The spindle is responsible for holding and rotating the cutting tools, making it crucial for the milling process.
Adjustability and Versatility
The milling head can be adjusted vertically and horizontally, which offers precision in making angular cuts. The motor within the milling head is typically a high-torque motor designed to handle various cutting tools and materials.
Spindle
The spindle is a critical part of the milling machine that holds and rotates the cutting tools. It is driven by the motor and can be adjusted to various speeds. The spindle speed is crucial for cutting different materials effectively. The spindle is mounted on the milling head and moves up and down, making it essential for the drilling and milling operations.
Role in Milling Operations
The spindle not only holds the cutting tools but also contributes to the precision of the cuts. It can be set to different speeds, depending on the material being worked on, making it flexible for various machining tasks.
Table
The table is another vital part of the milling machine where the workpiece is clamped in place. The table moves both horizontally and vertically, offering adjustable positioning for the workpiece. Made of high-strength material, the table ensures durability and supports various clamping mechanisms for securing the workpiece.
Flexibility and Precision
The tables flexibility in movement is essential for achieving precision in milling operations. With a series of T-slots, the workpiece can be secured firmly, providing stability during the milling process.
Quill
The quill is another crucial part of the milling machine, which holds the cutting tools. The quill can move vertically, allowing controlled depth cuts. The quill is particularly essential for operations requiring high precision and intricate detailing.
Controlled Depth Cuts
The quill offers the capability for controlled depth cuts, which is highly beneficial in detailed machining tasks. Ensuring the quill’s precision is vital for achieving accurate results.
Ram
The ram is the part of the milling machine that supports the milling head and allows it to move forward and backward. This movement is essential for positioning the head and making various types of cuts.
Maneuverability
The ram enhances the machine’s capability by allowing the milling head to cover multiple axes, making it versatile for different machining tasks. The movement of the ram supports the flexibility and functionality of the machine.
This Technological Insight
Investing time in understanding the essential parts of a milling machine is beneficial for industry QA professionals and operators. It’s here where the true power of milling technology is realized. From the sturdy base to the precise spindle, each component plays a tremendous role in making milling machines a cornerstone of manufacturing technology.

FAQs
What is the importance of the spindle in a milling machine?
The spindle holds and rotates the cutting tools, crucial for removing material from the workpiece. Its speed can be adjusted for different materials, making it highly significant in milling operations.
How does the power feed mechanism enhance productivity?
The power feed mechanism automates the table’s movement, reducing manual labor and ensuring consistent milling. This boosts productivity and provides more consistent results.
Why is the table’s flexibility important?
The table’s flexibility in movement allows for precise positioning of the workpiece, essential for accurate milling operations. It supports various clamping mechanisms, ensuring the workpiece stays secure during milling.