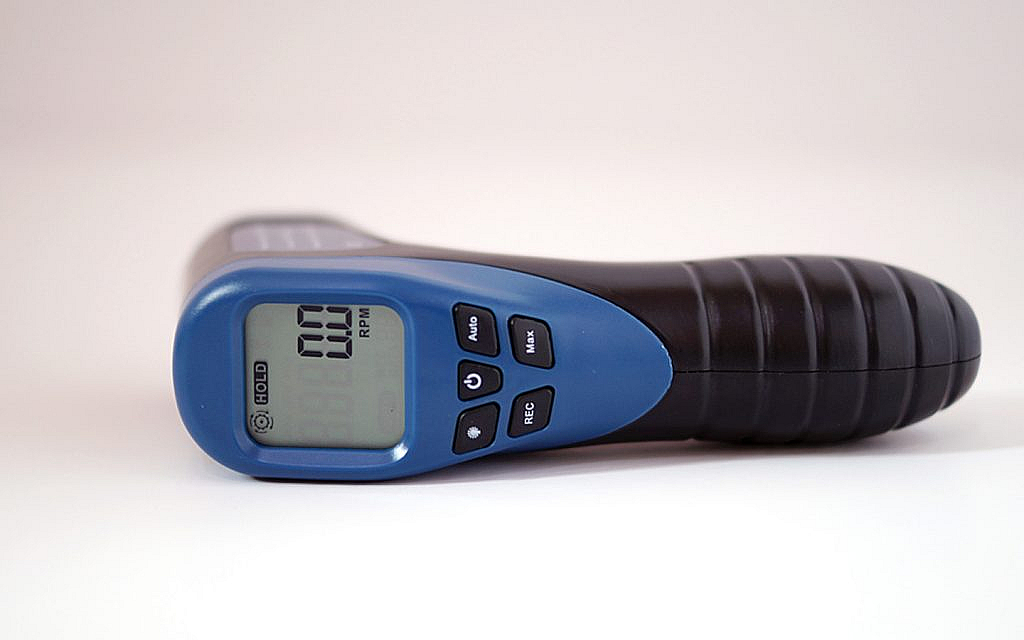
The world of diesel engines is fascinating, and understanding the various components that make them work can be incredibly insightful. One such crucial component is the diesel tachometer. How does a diesel tachometer work? This article dives into the mechanics and technology behind it, illustrating its importance for industry QA professionals. A diesel tachometer is an essential instrument that measures the rotational speed of the diesel engine’s crankshaft. It typically displays this speed in revolutions per minute (RPM), providing vital data for the efficient and safe operation of diesel engines.
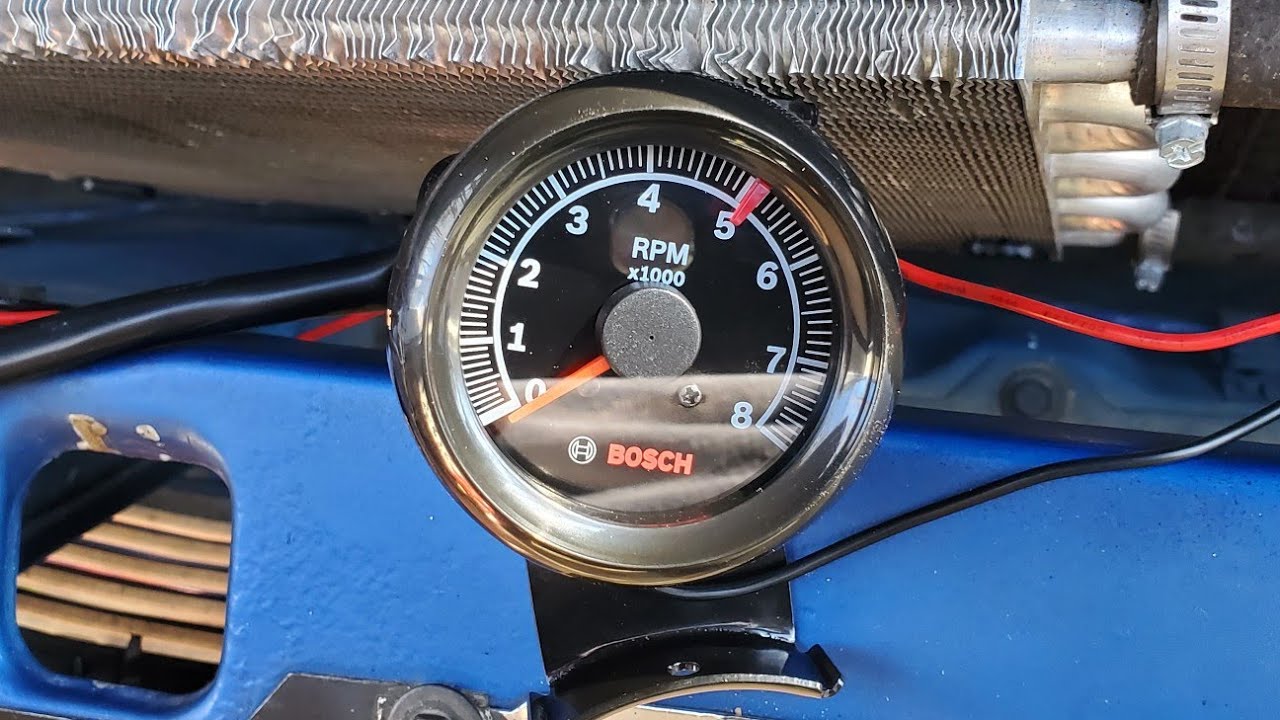

Introduction to Diesel Tachometers
A diesel tachometer is more than just a gauge; it’s a vital tool for diagnosing the health and performance of the diesel engine. Its primary function is to monitor the engine’s speed, ensuring that it operates within the optimal range. This is crucial for maintaining engine efficiency, minimizing wear and tear, and preventing potential damage.
The Importance of RPM Monitoring
Understanding engine speed is essential for several reasons. First, it helps prevent the engine from running too fast, which can cause excessive wear and damage. Second, it ensures that the engine is running efficiently, which can lead to fuel savings and increased longevity. Third, it provides valuable data for diagnostics and maintenance.
Components of a Diesel Tachometer
Sensor
The sensor is a pivotal part of the diesel tachometer. It detects the rotation of the engine’s crankshaft, converting this mechanical motion into an electrical signal. Common types of sensors used in diesel tachometers include magnetic sensors, optical sensors, and Hall effect sensors.
Signal Processor
The signal processor receives the electrical signal from the sensor and converts it into a readable format. This involves amplifying the signal, filtering out noise, and translating it into an RPM value. Advanced signal processors can also perform additional calculations and diagnostics.
Display
The display is the interface that presents the RPM value to the user. It can be analog, with a needle and dial, or digital, with an LED or LCD screen. The design of the display can vary depending on the application and user preferences.
Types of Diesel Tachometers
Mechanical Tachometers
Mechanical tachometers are the traditional type, using a cable and rotating magnet to measure RPM. They are robust and reliable but can be less accurate and more susceptible to wear over time.
Digital Tachometers
Digital tachometers use advanced electronics to measure and display RPM. They are more accurate, offer additional features, and are more durable in challenging environments. Digital tachometers are the standard choice for modern diesel engines.
Installation of Diesel Tachometers
Pre-installation Checks
Before installing a diesel tachometer, it’s essential to check the compatibility of the sensor and signal processor with the engine type. Additionally, ensure that all electrical connections are secure and that the tachometer is calibrated correctly.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
- Choose an appropriate location for the sensor and attach it securely to the engine.
- Run the wiring from the sensor to the signal processor, ensuring that it’s protected from heat and mechanical damage.
- Connect the signal processor to the display unit and secure all wiring connections.
- Calibrate the tachometer according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Test the tachometer to ensure accurate readings and troubleshoot any issues.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the diesel tachometer is crucial for its longevity and accuracy. This includes cleaning the sensor, checking connections, and recalibrating the device periodically.
Common Issues and Solutions
Several common issues can affect diesel tachometers, such as signal interference, faulty sensors, and display errors. Diagnosing these problems typically involves checking the sensor alignment, verifying electrical connections, and ensuring the signal processor is functioning correctly.
Advanced Features in Modern Diesel Tachometers
Data Logging
Modern diesel tachometers often come with data logging capabilities, allowing users to record engine performance over time. This data can be invaluable for diagnostics and maintenance planning.
Wireless Connectivity
Advanced tachometers may offer wireless connectivity, enabling real-time monitoring and data transmission to remote devices. This can be particularly useful for fleet management and remote diagnostics.
Integrated Diagnostics
Some tachometers include integrated diagnostic features, providing real-time alerts and recommended actions for any detected issues. This enhances the overall maintenance and reliability of the engine.
Applications of Diesel Tachometers
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, diesel tachometers are used to monitor engine performance in cars, trucks, and buses. They help ensure that engines run efficiently and that potential issues are addressed promptly.
Marine Industry
Marine vessels, including ships and boats, use diesel tachometers to monitor engine speed and performance. Accurate RPM readings are crucial for safe and efficient vessel operation. Read More
Industrial Equipment
Diesel engines power various industrial equipment, including generators, pumps, and compressors. Diesel tachometers help maintain optimal performance and prevent costly downtime. Read More
Benefits of Using Diesel Tachometers
Enhanced Engine Efficiency
By providing accurate RPM readings, diesel tachometers help ensure that engines operate within their optimal efficiency range. This can lead to fuel savings and reduced emissions.
Prolonged Engine Life
Monitoring engine speed helps prevent excessive wear and damage, extending the engine’s lifespan. Regular use of diesel tachometers can lead to significant cost savings in maintenance and repairs.
Improved Safety
Accurate RPM monitoring is crucial for safe engine operation. Diesel tachometers help prevent over-revving, which can lead to catastrophic engine failure and potential safety hazards.
Case Study: Diesel Tachometers in Fleet Management
Fleet management companies can greatly benefit from the use of diesel tachometers. By monitoring engine performance across their fleet, they can identify issues early, schedule maintenance proactively, and optimize fuel consumption. This leads to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved overall performance. Read More
Future Trends in Diesel Tachometers
Integration with IoT
The integration of diesel tachometers with the Internet of Things (IoT) is a significant future trend. This allows for real-time data transmission, remote monitoring, and advanced analytics.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) can enhance the functionality of diesel tachometers by providing predictive maintenance and real-time diagnostics. AI algorithms can analyze data trends and alert users to potential issues before they become critical.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diesel tachometers are crucial tools for monitoring and maintaining the performance of diesel engines. From their basic function of measuring RPM to advanced features like data logging and wireless connectivity, these devices offer tremendous value to industry QA professionals. By understanding how diesel tachometers work, professionals can ensure the efficient, safe, and reliable operation of diesel-powered equipment.
FAQ
What is the primary function of a diesel tachometer?
The primary function of a diesel tachometer is to measure the rotational speed of the engine’s crankshaft in RPM, providing crucial data for engine efficiency and safety.
How do digital and mechanical diesel tachometers differ?
Mechanical tachometers use a rotating magnet and cable system to measure RPM, while digital tachometers use advanced electronics for greater accuracy and additional features.
Why is RPM monitoring important for diesel engines?
RPM monitoring is important for preventing engine over-revving, ensuring efficient operation, and enabling early detection of potential issues, which can prolong engine life and reduce maintenance costs. High-speed Inspections
