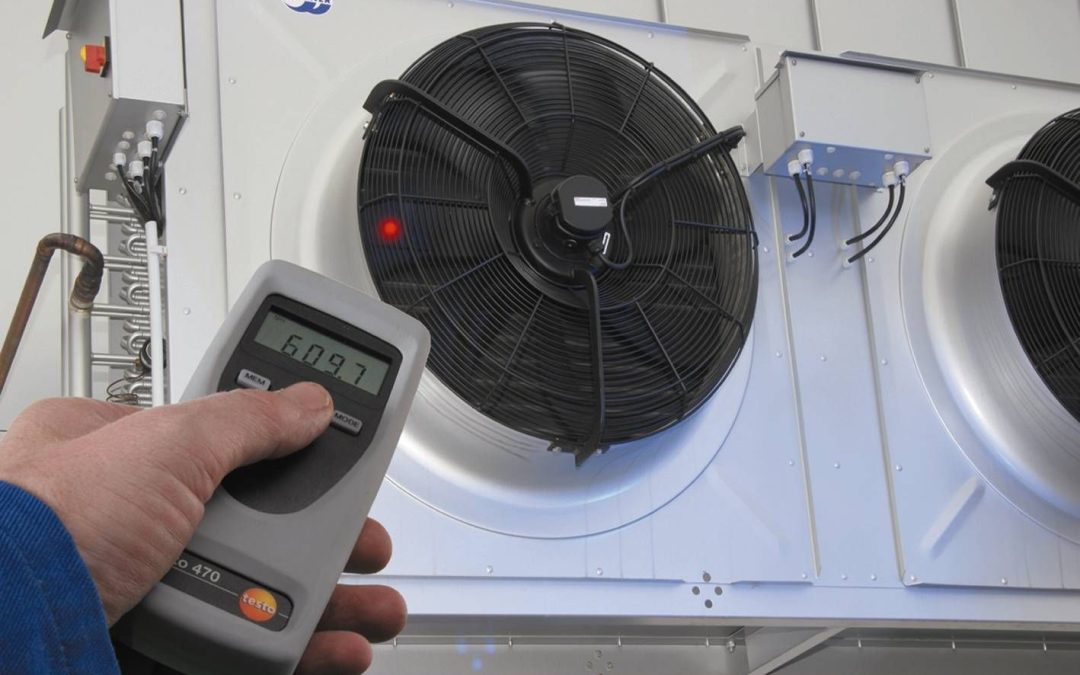
The tachometer is a crucial instrument used in various industries to measure the rotation speed of an object. It provides readings in revolutions per minute (RPM), serving as an essential component for numerous applications. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a curious beginner, understanding how to test a tachometer to see if it works is fundamental for ensuring its functionality and accuracy.
Proper testing of a tachometer guarantees that it delivers precise readings, which are vital for maintaining the efficiency and safety of machinery. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the steps involved in testing a tachometer and ensure it’s working correctly.
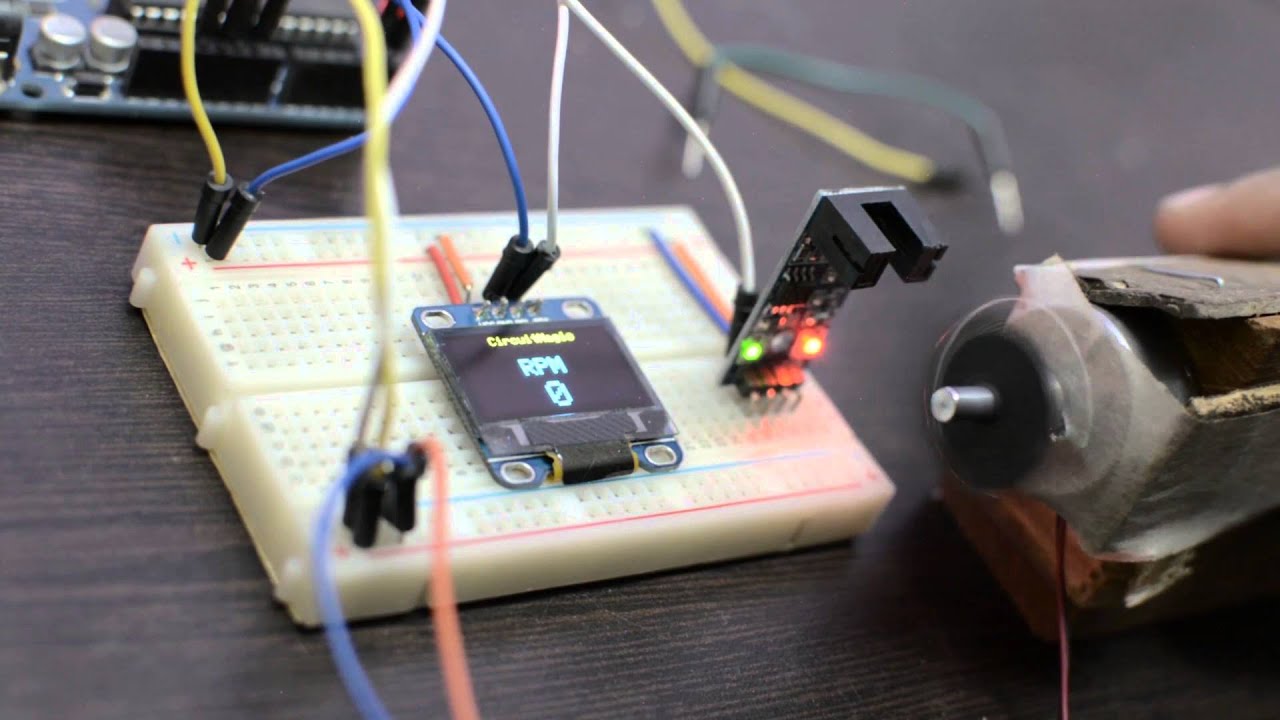
Understanding the Mechanics of a Tachometer
What is a Tachometer?
A tachometer is a device that measures the speed of rotation of a shaft or disk. It is commonly used in engines and other machinery to monitor performance and ensure optimal functioning.
Types of Tachometers
- Analog Tachometers
- Digital Tachometers
- Contact Tachometers
- Non-Contact Tachometers
Preparation for Testing a Tachometer
Gathering Necessary Tools and Equipment
Before testing a tachometer, you need to gather the tools and equipment required. This typically includes a multimeter, power supply, connecting wires, and the tachometer itself.
Safety Precautions
Always follow safety protocols when working with electrical instruments. Ensure the power is turned off before making any connections, and wear appropriate protective gear.
Step-by-Step Guide on Testing a Tachometer
Initial Inspection
Start with a visual inspection of the tachometer. Check for any physical damage, loose connections, or signs of wear.
Setting Up the Tachometer
Connect the tachometer to a power source, ensuring all connections are secure. Follow the manufacturers instructions for proper setup.
Using a Multimeter
Use a multimeter to measure the output voltage of the tachometer. Compare this reading with the manufacturers specifications to verify accuracy.
Testing RPM Readings
Run the machinery and observe the RPM readings on the tachometer. Ensure the readings are stable and match the expected values.
Recording Results
Document all readings and observations during the testing process. This data will be useful for future reference and troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Common Tachometer Issues
Inconsistent Readings
If the tachometer provides inconsistent readings, check for loose connections or interference from other electronic devices.
No Readings
If the tachometer shows no readings, verify the power supply and connections. Ensure the sensor is properly aligned with the rotating object.
Erratic Behavior
Erratic behavior may indicate a faulty tachometer. Consider replacing the device if it continues to malfunction after troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Testing a tachometer is a critical task that ensures its accuracy and reliability. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently test your tachometer and verify its functionality. Remember to conduct regular maintenance and inspections to keep your equipment in top condition.
For more information on tachometer testing and other related topics, visit the technical article.

FAQ
What is the primary purpose of a tachometer?
A tachometer measures the rotation speed of an object, usually in revolutions per minute (RPM).
Can a faulty tachometer be repaired?
In some cases, a faulty tachometer can be repaired. However, if the damage is extensive, it may be more cost-effective to replace the device.
How often should a tachometer be tested?
It is recommended to test a tachometer regularly, especially before critical operations. Regular testing helps maintain accuracy and reliability.
Explore more about Paint Inspections and Genetic Analysis on Strobox.ai.
